Renewable energy has become essential in our journey toward a sustainable future. With climate change and environmental issues causing great inconvenience to our lives today, renewable energy sources have emerged as a smarter and cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels. This blog explores some of the most common renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass. Each source brings unique advantages, helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a cleaner world.
- Solar Energy
- Sustainable and Abundant: The sun provides an almost limitless supply of energy. Solar power is available everywhere the sun shines, making it a dependable source of energy.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance, making solar energy cost-effective in the long run.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar power does not release harmful emissions, making it one of the cleanest forms of energy.
- Weather-Dependent: Solar panels only work when the sun is out, which makes them less effective on cloudy days or at night.
- High Initial Costs: While prices have dropped, the installation of solar panels can still be costly. This can make it challenging for some households or businesses to invest in solar power.
- Wind Energy
- Renewable and Sustainable: Wind energy is a naturally occurring resource that does not deplete over time, making it sustainable.
- Low Operational Costs: Like solar power, wind energy has low maintenance requirements after installation.
- Space Efficient: Wind turbines can be placed on farmland or offshore, allowing energy production without taking up much land space.
- Dependent on Wind Conditions: Wind turbines rely on steady winds, which are not always available in all regions.
- Impact on Wildlife: Birds and bats are sometimes affected by the presence of wind turbines, although research and technology are evolving to reduce this impact.
- Noise and Aesthetic Concerns: Some people find the noise and appearance of wind turbines disruptive, especially when placed close to residential areas.
- Hydropower
- Reliable and Consistent: Unlike solar and wind, hydropower can generate electricity consistently as long as there is water flow.
- High Efficiency: Hydropower plants are highly efficient, with some converting over 90% of the available energy in water into electricity.
- Flexible Energy Production: Hydropower can easily adjust electricity production to meet demand, making it an excellent resource for peak times.
- Environmental Impact: Building large dams can disrupt local ecosystems and displace communities.
- Geographic Limitation: Hydropower requires specific geographical features, such as the presence of rivers or lakes, which are not available in every location.
- Risk of Droughts: During dry seasons, water levels may drop,reducing electricity production.
- Geothermal Energy
- Consistent Energy Supply: Geothermal energy provides a constant supply of power, regardless of weather conditions.
- Small Environmental Footprint: Geothermal power plants typically occupy a small amount of land, causing minimal disruption to surrounding areas.
- High Efficiency: Geothermal energy is highly efficient, converting a significant amount of the earth’s heat into usable energy.
- Location-Specific: Geothermal power requires specific geological conditions, often found near tectonic plate boundaries or volcanic areas.
- Potential for Earthquakes: Drilling for geothermal energy can sometimes cause small earthquakes, although this is rare and generally low in intensity.
- Initial Costs: The drilling and setup required for geothermal plants can be costly, although operational costs are low once established.
- Biomass Energy
- Reduces Waste: Biomass energy uses waste materials, turning them into a valuable source of power and reducing the need for landfill space.
- Carbon Neutral: While biomass burning releases carbon dioxide, it is considered carbon neutral because the plants absorb a similar amount of carbon during their growth.
- Versatile: Biomass can be used for heat, electricity, and even transportation fuel, making it a highly versatile energy source.
- Land and Water Usage: Growing crops specifically for biomass can require large amounts of land and water, impacting local resources.
- Air Pollution: While biomass is carbon neutral, burning it can release other pollutants. New technologies are being developed to minimise this impact.
- Efficiency Concerns: Biomass energy can sometimes be less efficient compared to other renewable sources, especially when considering the energy required to produce and transport biomass materials.

Solar energy is one of the most widely recognised renewable energy sources. It harnesses the sun’s energy through solar panels, converting sunlight into electricity. This energy can power homes, businesses, and even large power grids.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Limitations of Solar Energy
Wind energy harnesses the power of the wind through turbines that convert kinetic energy into electricity. This energy source has been growing in popularity due to its effectiveness and clean operation.
Benefits of Wind Energy
Limitations of Wind Energy

Hydropower is one of the oldest sources of renewable energy, using water to generate electricity. Typically, this involves using a dam to control water flow, which spins turbines to produce electricity.
Benefits of Hydropower
Limitations of Hydropower

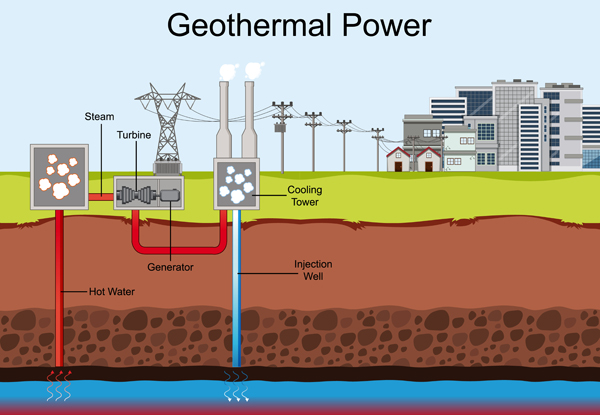
Geothermal energy taps into the earth’s internal heat to generate electricity. This heat is often accessed through geothermal power plants, which use steam from hot water reservoirs below the earth’s surface.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy
Limitations of Geothermal Energy
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and waste. These materials are burned or converted into biofuels, generating electricity or heat.
Benefits of Biomass Energy
Limitations of Biomass Energy

The Importance of Renewable Energy in Our Future
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass play a vital role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing down climate change. Transitioning to these sources helps reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to pollution and global warming.
Switching to renewables also provides countries with energy independence. By investing in local energy sources, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, which can be expensive and subject to market fluctuations.
Conclusion
Renewable energy sources offer cleaner, sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, helping us work towards a greener, healthier planet. Each type of renewable energy has its strengths and limitations, but together, they provide a balanced approach to tackling environmental challenges. As renewable technology continues to advance, it becomes easier for individuals, communities, and governments to adopt these solutions.
In Centre Point School (CPS), teaching students about renewable energy encourages awareness of environmental responsibility from a young age. By understanding the importance of clean energy, students at CPS are empowered to make informed choices and contribute to a sustainable future.